Creating a Nature Positive Future: The Contribution of Protected Areas and Other Effective Area-Based Conservation Measures
The United Nations Development Programme (UNDP), the Secretariat for the Convention on Biological Diversity, and the UN Environment Programme—World Conservation Monitoring Centre (UNEP-WCMC) recently published a report “Creating a Nature Positive Future: The Contribution of Protected Areas and Other Effective Area-Based Conservation Measures” which calls for an essential focus on the quality aspects of Protected and Conserved Areas.
According to this report, more equitable, representative, and effective Protected Areas (PAs) and other effective area-based conservation measures (OECMs) are imperative elements for stopping and reversing the continuing loss of global biodiversity.
The top 5 leading drivers of global biodiversity loss shown in the report are:
- changes in land and sea use
- direct exploitation of organisms
- climate change
- invasive alien species
- pollution
Nature positive future
It is clear that the contribution of PAs and OECMs is a crucial component for achieving a “nature positive” future, but what does it exactly mean?
Nature positive refers to actions that increase resilience of the planet and biodiversity, as well as societies, with the aim of creating a paradigm shift to reduce the loss of nature, secure nature’s contributions critical for humanity, and enhance sustainable socio-economic development.
Biodiversity and conservation benefits from Protected Areas and other effective area-based conservation measures
As shown in the report, PAs and OECMs contribute to biodiversity conservation and other benefits including water and food security, climate mitigation, disaster risk reduction, livelihoods, health, and human well-being.
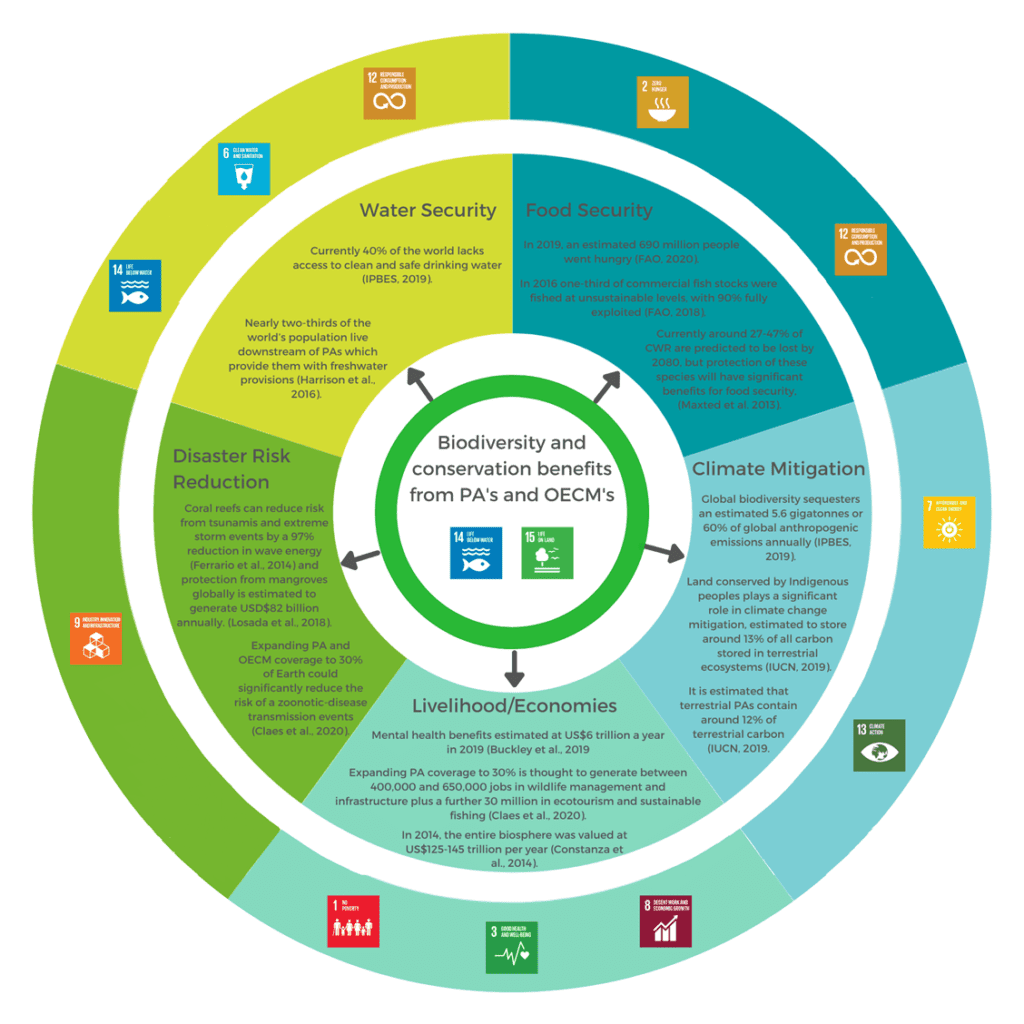
The direct benefits and co-benefits provided by PAs and OECMs and the contribution of these towards the Sustainable Development Goals. Image from the report: CREATING A NATURE POSITIVE FUTURE THE CONTRIBUTION OF PROTECTED AREAS AND OTHER EFFECTIVE AREA-BASED CONSERVATION MEASURES
Moreover, in order to achieve a nature-positive future, the report highlights three important considerations that can improve the quality of the PAs and OECMS:
- Increase coverage, prioritizing representativeness, connectivity, and the conservation of areas important for biodiversity; equitable expansion; and effective management and quality outcomes in PAs and OECMs
- Scale-up recognition of the contribution of Indigenous Peoples and Local Communities (IPLCs) territories, lands and waters and secure tenure rights
- Embed PAs and OECMs into national policies and decision-making frameworks
Shifting the focus on the quality of protection of Protected and Conserved Areas can significantly contribute to the achievement of the 2030 Sustainable Development Goals. Finally, by collectively working on issues highlighted by this report, we can achieve the CBD’S 2050 Vision of living in harmony with nature:
“By 2050, biodiversity is valued, conserved, restored and wisely used, maintaining ecosystem services, sustaining a healthy planet and delivering benefits essential for all people.”
The report in several languages can be found and downloaded here.