A review of EUROPARC Conference 2016 – Report is out!
The EUROPARC Conference 2016 was host and organised by the Parc Jura vaudois, in Switzerland.
The Conference brought together over 300 delegates from 36 European countries, who had the chance to learn, exchange experiences and discover interesting examples from all over Europe. Under the theme “We are Parks”, we examined the role of the people in our parks – from fund raising to governance models.
The Conference report is now available and it includes an overview of all moments of the Conference:
- General Assembly 2016
- Keynote speakers presentations
- Tutorials and Workshops conclusions
- President’s meeting
- Martekplace
- Inhabitants Party
- Award Ceremonies: Transboudanry Parks Programme, Alfred Toepfer Medal and Alfred Toepfer Natural Heritage Scholarship
The bottom-up democratic model of parks in Switzerland helped us consider how communities can and do participate in the governance of our parks, while inspiring keynote speakers from the European Environmental Agency and the IUCN gave us interesting overviews on what’s going on in Europe and in the World. See the Plenary Session page to download all keynote speakers’ presentations.
Parks are ideal laboratories, playgrounds for democratic and participatory processes (regardless of the national context : Swiss approach or other European approaches). There is a need to transmit the importance of long term processes in order to improve our enviromental conditions for nature and mankind.
Watch the film of EUROPARC Conference 2016
Sustainable Agriculture: the importance of building partnerships
Autumn Sunset at Lough Tay, Ireland © Ronan
Article issued by Brian Dunne,
extracted from EUROPARC Journal Protected Areas In-Sight 2016
Wicklow Uplands Council; twenty years of consensus and partnership
Located immediately beside Dublin, County Wicklow is renowned as the ‘Garden of Ireland’ due to the diversity and quality of its landscape. Rolling mountains, conical peaks, glaciated valleys and deep lakes characterise the Wicklow Uplands, the largest upland area in Ireland. Every element of Wicklow’s landscape has the imprint of human activity.
Established in 1997, Wicklow Uplands Council is a sustainable development NGO which formed in response to growing pressures facing the sustainability of the uplands. The Council works for the sustainable use of the uplands in consensus and partnership with those who live and work in the region and those who use it for recreational purposes. Membership is represented by local and national organisations and individuals. Consensus is the cornerstone of the organisation with no single decision voted upon since its inception.
The importance of local partnerships
The Council recognises the necessity for collaboration and partnership in all projects in order to achieve sustainability and is committed to work with all stakeholders in the spirit of Local Agenda 21. Supporting upland farmers and promoting the best management of our upland habitats is one of a number of ongoing projects.
A decline in traditional hill farming, due in part to restrictions in vegetation management has resulted in overgrown habitats and a decline in overall upland biodiversity. A working group comprised of local farmers, farming organisations and statutory partners was formed to address these issues. The group lobbied for the provision of a Sustainable Agri-Environmental Scheme which would provide optimal conditions for upland biodiversity through hill farming with farmers remunerated for services provided. There is now provision for ‘Locally Led Agri-Environment Schemes’ under Pillar II of the Rural Development Programme and a call for applications for upland areas is expected imminently.
The bottom-up approach to upland management employed by Wicklow Uplands Council provides local perspective, engagement and energetic enthusiasm. These ideas are brought to statutory partners who can provide vital professional expertise and proficiency in legislative and funding frameworks. Project funding can vary but is typically sourced from EU and national programmes.
The Council continues to develop the partnership concept in many other innovative ways. Establishing partnerships is a challenging but rewarding process and land management partnerships in particular will remain at the core of the Council’s work.
 Further details on Wicklow Uplands Council and all our projects can be found on www.wicklowuplands.ie
Further details on Wicklow Uplands Council and all our projects can be found on www.wicklowuplands.ie
Are you working in the field of Sustainable Agriculture within your Park?
The EUROPARC Federation is looking for members who have agriculture production in or around their Protected Area, and want to understand and develop more sustainable agriculture practices. The invitation is to join the Siggen Seminar, a free training for members, that will take place in north Germany, from the 10-13th March.
All information is available here and if you are interested in participating register before the 24th February!
Gathering of fungi as a tool for biodiversity conservation in Plitvice Lakes National Park
Photo by Eduardo Batista, Plitvice Lakes National Park, Croatia
Gathering of fungi as a tool for biodiversity conservation in Plitvice Lakes National Park, Croatia
article issued by Eduardo Batista
Every year, the Alfred Toepfer Natural Heritage Scholarship (ATS) supports the work of young conservationist in protected areas across Europe. Eduardo was one of the winners of the Scholarship in 2015.
The Plitvice lakes National Park in Croatia is well known worldwide for the unique lakes and waterfalls. The fauna and flora of the park enrich even more the uniqueness of this protected area. With almost 1500 plant taxa and with a rich local animal life, the Plitvice National Park is an example of environmental education for more than one million visitors per year.
Why a study about fungi?
Recent studies show us that 10-20% of European mushrooms may be threatened and few countries had developed a conservation policy regarding macrofungi. National parks and protected areas in some regions are the unique natural contact that citizens have and it’s important to use them as an educational resource to promote their conservation.
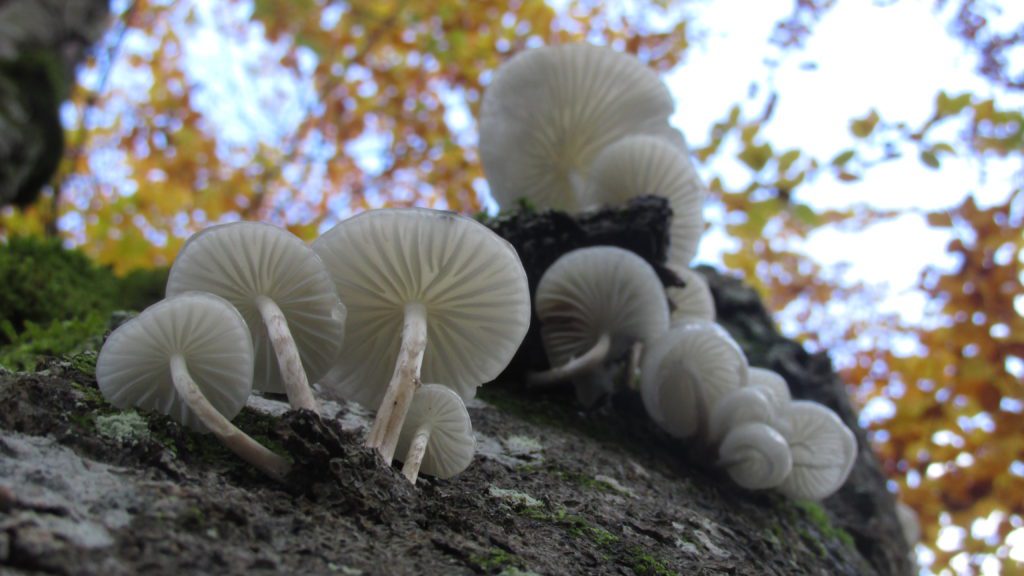

Oudemansiella mucida, Photo by Eduardo Batista, Plitvice Lakes National Park, Croatia
With the Scholarship awarded by EUROPARC Federation and the Alfred Toepfer Stiftung, I aimed to work at 2 levels:
- CONSERVATION – Elaboration the fungi checklist of Plitvice Lakes National Park and draw up a guide of best practices of fungi conservation
- EDUCATION – understand how the macrofungi community can help to enrich the educational value of the existing trails in the park and what a normal visitor can expect and learn from the mycological resources
One of the trails analysed by Eduardo Batista, Plitvice Lakes National Park, Croatia
During eight days, all the existing trails were analyzed based on an evaluation framework. In the final report, five trails are discussed, regarding their mycological interest and management practices are recommended.
In the five selected trails, 45 different macrofungi species were identified without leaving the trails. With this visit, I expected to raise the awareness not only of visitors but also of local staff – increasing their awareness of the existent mycological resources in the park and to create a framework of discussion for new management and conservation practices respecting the fungi biodiversity.
From a management perspective, the park implemented a “non-dead wood removal policy” that allows a significant decomposition along the park. This dead wood is essential to maintain and promote several ecological processes. However, if this “dead wood” would be located near the trails it would allow the visitor to have more contact with several saprophytic fungi. Is important to create an enjoyable experience without the need of leaving the trails. This action of promoting biodiversity near the trails is very important taking into consideration the huge number of visitors per year.
Fungi: future considerations for European Protected Areas
In 2007, the European Council for Conservation of Fungi (ECCF) presented a document entitled “Guidance for the Conservation of Mushrooms in Europe” where the efforts to identify and report conservation actions of the European macrofungi community were evaluated. According to this document, most European countries have produced fungal Red-list and more than 5 500 different macro fungi are red-listed in at least one European country. These numbers show us that 10-20% of European mushrooms may be threatened, putting the fungi conservation as a priority.
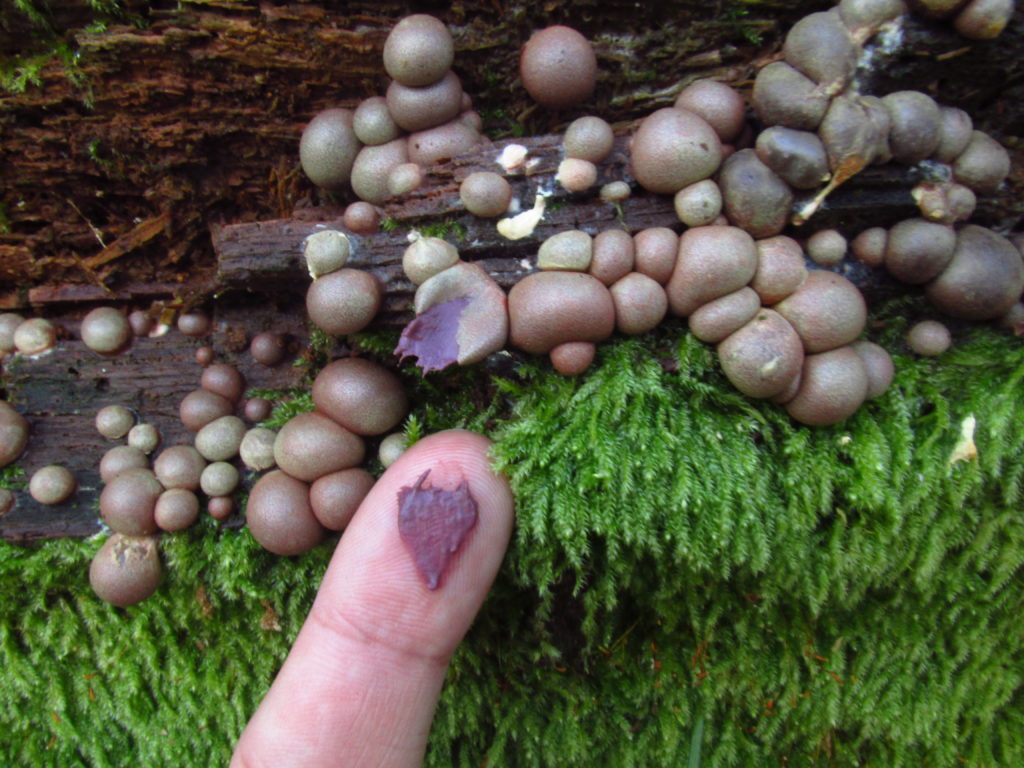

Photo by Eduardo Batista, Plitvice Lakes National Park, Croatia
All protected area should describe their fungi community and in case of forest management activities, the impact should be studied. Only after a long-term study, it will be possible to analyse if there are some endangered species and which factors are leading to that. After that, conservative measures regarding fungi diversity should be included in the management plan of each organisation/protected area.
to do list for Parks:
- describe their fungi community in a long-term study
- analyse possible endangered species
- develop educational information to be provided to visitors raising the importance of the fungi world.
Download Eduardo’s full report
For more information, you can consult the “European Charter on Fungi- Gathering and Biodiversity -2013” prepared by Scott Brainerd and Sarah Doornbos on behalf of the Bern Convention.
Engaging Sustainable Partners – Montseny Nature Park
Charter Partners awarded by Montseny Nature Park, December 2016
Montseny is one of the most visited Sustainable Destinations in Catalonia, Spain, who started its journey with the European Charter for Sustainable Tourism in Protected Areas (ECST) in 2011. In December 2016, Montseny renovated their commitment with Sustainable Tourism and was re-awarded in Brussels, at the Charter Award Ceremony.
Montseny is successfully implementing Charter Part II – Sustainable Partners, and have been recognised by their work with the local stakeholders. We’ve asked Elisabet Ros Garriga, technician of the Park and responsible for the ECST implementation, to tell us more about their engagement strategy.
article issued by Elisabet Ros Garriga
A glimpse of Montseny Nature Park
Parc Natural del Montseny is located in the Provinces of Barcelona and Girona, in Catalonia, Spain. It is one of the oldest natural Parks in Catalonia and one of the most known of the region. The Park has 31,063.90 ha. and 85% of the Park’s surface is privately owned. Montseny was designated as Biosphere Reserve by UNESCO in 1978 and extended in 2014 to cover an area of 50.166,63 ha.
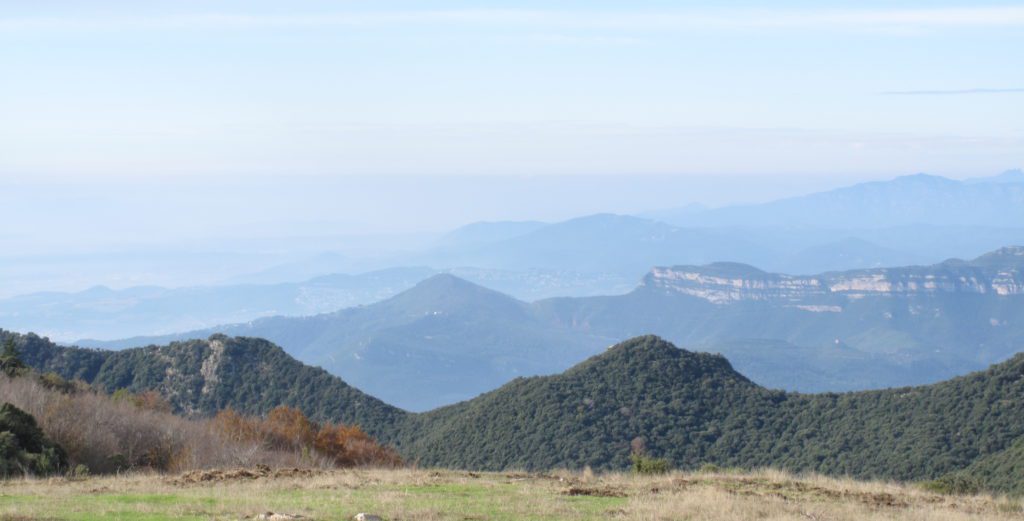

Parque Natural Montseny © JA Atauri
Montseny is the largest and highest massif of the pre-littoral mountain range: its relief starts with elevations of less than 200 metres to just over 1,700 m. The differences in humidity and temperature of the diverse environments make it a natural area extraordinarily rich in vegetation. In the lower areas we can find typically Mediterranean formations of vegetation; in the rainy mid-mountain area, mountain holm oak forests and oak woods; in the areas above 1,000 metres, beech woods and fir trees and on the peaks, scrubland and alpine meadows. The Park is less than one hour from the city of Barcelona (1.6 million inhabitants) and its metropolitan area (1.6 million inhabitants). As a result, the Park has a high number of
The Park is less than one hour from the city of Barcelona (1.6 million inhabitants) and its metropolitan area (1.6 million inhabitants). As a result, the Park has a high number of visitors estimated from 75,000 to 1 million per year.
The Charter for Sustainable Tourism: working together
The Charter Area is much larger than the Park, covering 27 municipalities: 18 belong to the Park whilst the others are completely outside the Park but they have a traditional link to the massif of Montseny.
Montseny was awarded the ECST for the first time in 2011; fulfilling Europarc’s requirements. In 2015, we began to work on the Charter renovation.
During the renovation process, the Permanent Forum met 4 times, gathering a high number of members: participation of private and public sector was about 40 participants in each session. To underline is that during the renovation process, the focus was set on ensuring real participation for the next Charter period. Therefore, municipalities were asked to formally arrange this commitment by appointing a “Charter person”.
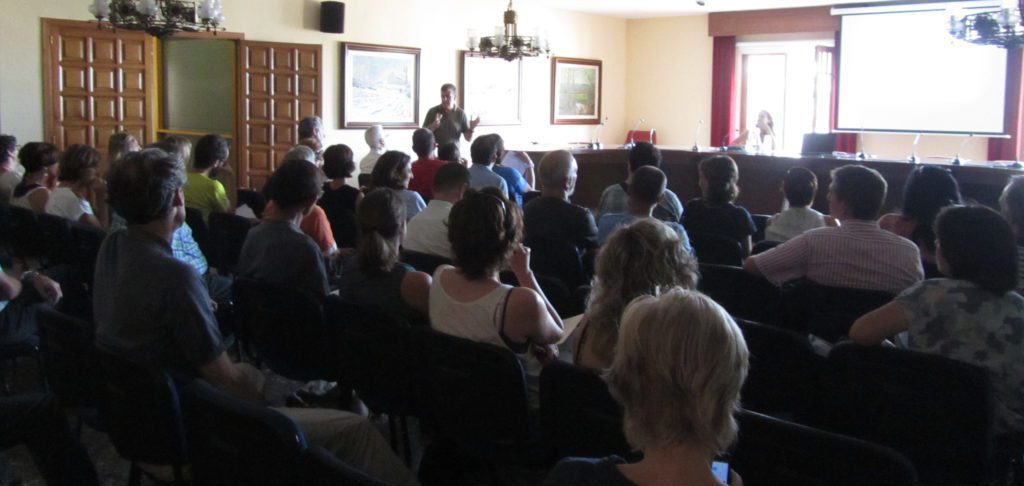

ECST meeting with partners
Involvement and Recognition
On May 2016 took place the renovation audit which let the verifier Amanda Guzmán get closer to the main strengths of the ECST in Montseny as well as to the challenges that the area is still facing. The Verifier’s report congratulates the Charter area for its improvement in communication and its work in cooperation with and amongst different stakeholders. The report also highlights the involvement of the Associació d’Empresaris Turístics del Montseny (Association of Tourism Businesses in Montseny) as an organisation that brings together the entire scope of the ECST.
Sustainable Partners: Implementing Charter Part II
Regarding Charter Part II – Sustainable Partners in Charter Areas, the first batch of 10 companies were awarded the Charter in December 2014 whilst the second batch of 7 enterprises was recently awarded – December 2016.
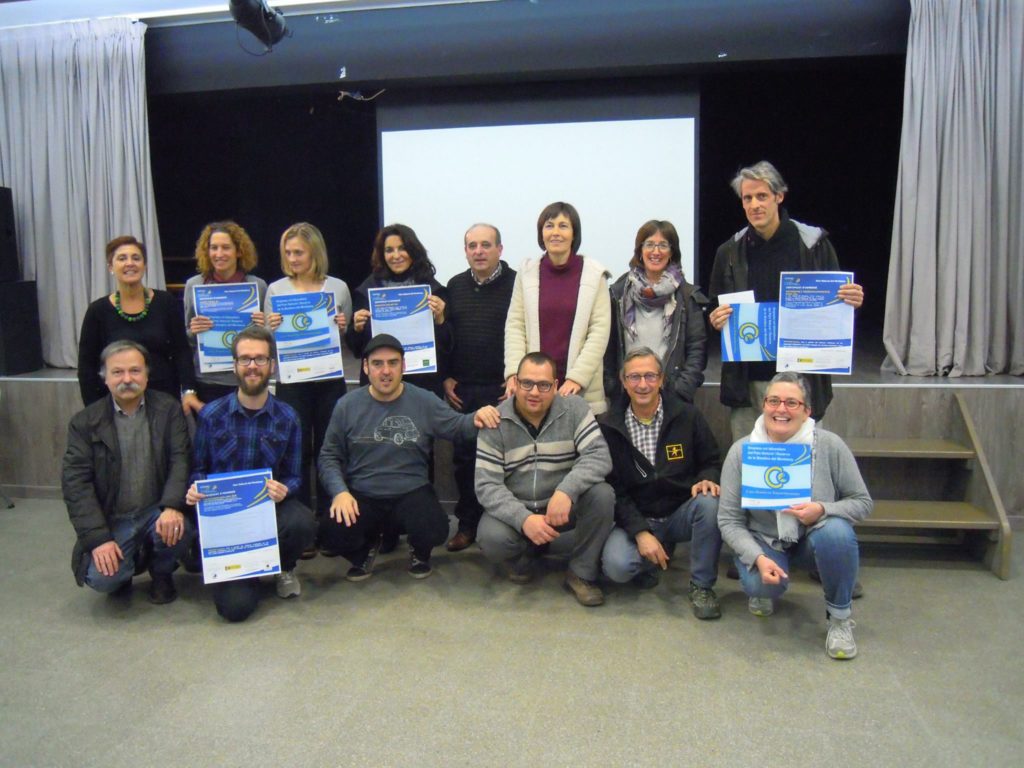

Charter Partners awarded by Montseny Nature Park, December 2016
Park has been working on dissemination actions, positive discrimination of these companies as suppliers and funding of the Charter Part II process itself. Businesses are restaurants, hotels and rural guest houses, guiding and educational services as well as local producers offering guided visits to their farms.
The companies have also created a working group where joint action on communication activities is currently discussed. The Partners awarded have a dedicated page on Montseny’s website: http://parcs.diba.cat/web/turisme-sostenible-als-espais-naturals/restaurants1
For implementing and monitoring Charter Part I and II an external consultant company (REPTE) has been hired for developing a Charter Secretariat. This combination had good results and it was considered “positive to have an external and expert view during the process” in the Verification report.
For more information about the Charter in Montseny contact p.montseny.cets @ diba.cat.


